Blockchain and Supply Chain Management: A New Era of Transparency and Efficiency
In the intricate world of supply chain management (SCM), where numerous stakeholders interact to deliver goods from manufacturers to consumers, efficiency and transparency are crucial. Traditional supply chains often struggle with issues like data silos, fraud, and inefficiencies, which can impact cost, speed, and reliability. Enter blockchain technology—a transformative tool with the potential to address these challenges and revolutionize supply chain management. This article explores how blockchain is reshaping supply chains, the benefits it offers, and the challenges associated with its implementation.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger technology where transactions are recorded across a distributed network of computers. Each transaction is bundled into a “block” and linked to the previous block, forming a “chain.” This structure creates an immutable, secure record of all transactions, which is visible to all participants in the network.
Key features of blockchain include:
Decentralization: No single entity controls the blockchain; instead, it is maintained by a network of nodes, reducing the risk of centralized failures.
Immutability: Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring a permanent and trustworthy record.
Transparency: All participants in the blockchain network have access to the same data, enhancing visibility and accountability.
Traditional Supply Chain Challenges
Supply chains are complex ecosystems involving multiple entities such as suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and customers. Traditional supply chains face several challenges:
Lack of Transparency: Information is often fragmented and siloed within individual organizations, leading to a lack of visibility across the entire supply chain.
Inefficiencies: Manual processes and paper-based records can cause delays and increase the risk of errors.
Fraud and Counterfeiting: Ensuring the authenticity of products and preventing fraud is challenging, especially in global supply chains.
Traceability Issues: Tracking products from origin to end-user can be difficult, particularly in the event of recalls or quality issues.
Blockchain’s Impact on Supply Chain Management

Blockchain technology offers a range of solutions to address these traditional challenges, enhancing supply chain management in several key areas:
1. Enhanced Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain’s immutable ledger provides a single source of truth for all transactions within the supply chain. This transparency allows stakeholders to track the journey of products from raw materials to the final consumer.
For example, in the food industry, blockchain can trace the provenance of products, ensuring they are fresh and ethically sourced. Consumers can scan QR codes on products to access detailed information about their origins, handling, and quality. This level of transparency builds consumer trust and helps companies address food safety issues more efficiently.
2. Improved Efficiency and Reduced Cost
Blockchain technology can automate and streamline various supply chain processes through the use of smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute transactions, manage inventory, and trigger payments when predefined conditions are met.
For instance, a smart contract could automatically release payment to a supplier upon delivery of goods, reducing the need for intermediaries and paperwork. This automation not only speeds up processes but also reduces administrative costs and errors.3. Enhanced Security and Fraud Prevention
The decentralized nature of blockchain enhances security by reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access. Each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous one, making it nearly impossible to alter past records without detection.
In industries like pharmaceuticals and luxury goods, where counterfeiting is a significant issue, blockchain can verify the authenticity of products. Manufacturers and retailers can record product details on the blockchain, allowing consumers to verify authenticity and preventing counterfeit goods from entering the market.
4. Better Risk Management and Resilience
Blockchain can improve risk management and resilience in supply chains by providing real-time visibility and traceability. In the event of a disruption—such as a natural disaster, geopolitical issue, or supplier failure—stakeholders can quickly identify affected areas and implement contingency plans.
For example, if a supplier fails to deliver, blockchain’s transparency allows other participants to trace the issue and find alternative solutions swiftly. This capability enhances supply chain resilience and helps mitigate the impact of disruptions.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management

Several companies are already leveraging blockchain technology to enhance their supply chain operations:
1. Walmart
Walmart has implemented blockchain technology to track the provenance of food products. By partnering with IBM’s Food Trust blockchain network, Walmart can trace the journey of food items from farm to store in seconds, compared to days using traditional methods. This capability has improved food safety, reduced waste, and increased efficiency in the supply chain.
2. De Beers
The diamond industry faces challenges related to conflict diamonds and fraud. De Beers, a leading diamond company, uses blockchain to track the provenance of diamonds from the mine to the retail market. The blockchain ledger ensures that each diamond is sourced ethically and provides customers with confidence in the authenticity of their purchases.
3.Maersk and IBM
In collaboration with IBM, Maersk has developed TradeLens, a blockchain-based platform for managing shipping and logistics. TradeLens provides real-time tracking of cargo, automates documentation processes, and enhances collaboration among various stakeholders in the shipping industry. This system has streamlined operations and reduced paperwork, leading to significant cost savings.
Challenges of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
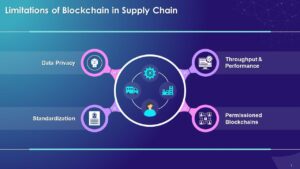
Despite its potential, implementing blockchain in supply chain management comes with several challenges:
1. Integration and Scalability
Integrating blockchain with existing supply chain systems can be complex and costly. Businesses must invest in technology and train staff to effectively use blockchain solutions. Additionally, scaling blockchain networks to accommodate large volumes of transactions and participants can be challenging.
To address these issues, developers are exploring solutions such as permissioned blockchains and layer-2 scaling technologies that enhance transaction throughput and reduce latency.
2.Data Privacy
While blockchain enhances transparency, it also raises concerns about data privacy. The immutable nature of blockchain means that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This can be problematic for supply chains where the ability to correct errors or update information is essential.
Privacy features, such as permissioned blockchains or advanced cryptographic techniques like zero-knowledge proofs, can help address these concerns by allowing for selective data sharing and protection.
3. Regulatory and Legal Issues
The regulatory landscape for blockchain technology is still evolving. Companies must navigate various legal and regulatory requirements related to data protection, intellectual property, and cross-border transactions. Staying compliant with these regulations is crucial for successful blockchain implementation.
4. Adoption and Change Management
Adopting blockchain technology requires significant changes to existing processes and systems. Businesses must manage the transition carefully, ensuring that all stakeholders are on board and that the technology is integrated smoothly into existing workflows. Change management strategies and stakeholder engagement are essential for successful adoption.
The Future of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management

As blockchain technology continues to evolve, its impact on supply chain management is expected to grow. Innovations such as blockchain-based digital identities, integration with the Internet of Things (IoT), and advancements in smart contracts will further enhance supply chain operations.
Blockchain’s ability to provide transparency, efficiency, and security positions it as a game-changer in supply chain management. Businesses that embrace this technology will likely gain a competitive edge, driving innovation and setting new standards for operational excellence.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by addressing longstanding challenges and unlocking new opportunities. From enhancing transparency and traceability to improving efficiency and security, blockchain offers a transformative approach to managing complex supply chains.
While there are hurdles to overcome, including integration, scalability, and regulatory compliance, the benefits of blockchain—such as reduced costs, increased trust, and better risk management—make it a compelling solution for modernizing supply chain operations. As the technology matures and adoption increases, blockchain could become a cornerstone of a more transparent, efficient, and resilient global supply chain.
